Company overview
Grubhub (NYSE: GRUB) is an online food delivery service that connects diners with nearby restaurants. Orders are placed online and are delivered to the user’s doorstep. Restaurants may carry out the delivery themselves or pay Grubhub to do so. The company has over 9.18 million active diners and 55,000 restaurant partners in over 1,100 cities across the US and the UK. The firm was founded in 2004 and later merged with Seamless, a competitor with a similar business model. The company went public on April 2014, trading at $34.00 per share. At market close last Friday (October 6, 2017), shares were trading at $51.29. GRUB does not pay dividends yet.
The company estimates its Total Addressable Market (TAM) to be $245bn dollars. $75bn of these are the delivery and pickup component of the US independent restaurant industry, which, in total, generates $200bn annually. The remaining $170bn are the potential takeout and delivery from restaurant chains. Even though it is already leading the industry, with just $2.5bn in gross food sales, the firm has much room for market penetration and revenue growth.
Grubhub’s main competitors are Uber and Amazon, who offer services like UberEATS and Amazon Restaurants, and are already large, established companies. Nevertheless, Grubhub has maintained its competitive leadership by acquiring smaller firms like Eat24, Foodler, LAbite, Bask Labs, Delivered Dish, and DiningIn, as well as setting up partnerships with the likes of Yelp and Groupon. Further, Grubhub has partnered with several restaurant chains, including Subway, TGI Friday’s, Red Robin, Buffalo Wild Wings, and Denny’s.
The three main revenue drivers for the business are: the number of active diners, daily average grubs (orders), and gross food sales. The firm discloses these in each quarterly report.
Future developments and Income forecasts
Grubhub is already well established in Tier 1, high-order-frequency markets like Manhattan, and is expanding into Tier 2-4 markets. These less saturated markets (Tier 2-4) offer significantly lower daily average grubs per active diner than Tier 1 markets. However, they remain profitable and represent a large amount of the overall addressable market. At some point in the near future, penetration in Tier 1 markets will have reached its peak, especially given the intense competition from Amazon and Uber, and so expansion in lower-tier markets will become essential for GRUB to maintain its leadership in the industry as a whole. GRUB has the ability to be competitive in these markets by being the first-mover and reaching them before Amazon and UberEATS, organically or via acquisitions. To achieve this, GRUB is investing heavily in marketing campaigns and trying to reach as many restaurants as possible. Chains are particularly helpful in this situation, as they have already developed an extensive presence in these markets.
To project revenues, assumptions were made for the growth in the number of Active Diners as well as three key ratios:
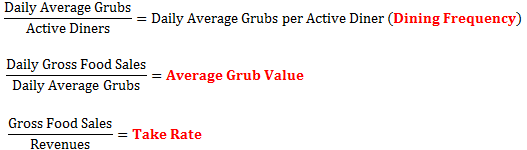
Dining Frequency: the frequency at which an Active Diner places orders – the inverse of this number is the average number of days between orders per Active Diner
Average Grub Value: average gross dollar amount per grub (order)
Take Rate: the proportion of gross sales that become revenue for GRUB
By making quarterly assumptions for Active Diner growth, Dining Frequency, Average Grub Value, and Take Rate, the revenue can be projected in four steps:

Below are revenue projections for conservative, base and strong scenarios based on guidance figures provided by GRUB. The base scenario assumes business will continue as normal, with modest revenue driver growth and unchanged expense margins. The conservative scenario assumes a significant revenue driver growth deceleration due to competition from Amazon Restaurants and UberEATS, as well as increased expense margins. The strong scenario assumes Grubhub significantly outperforms its competitors, with accelerating revenue driver growth and significant efficiencies of scale, resulting in lower expense margins.
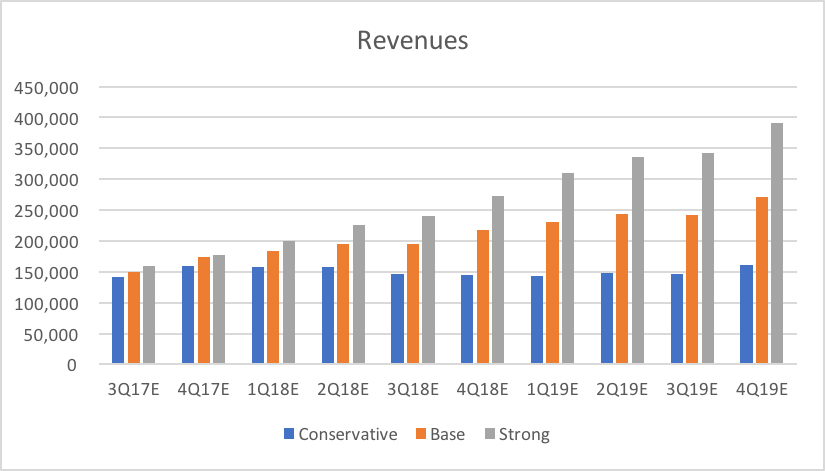
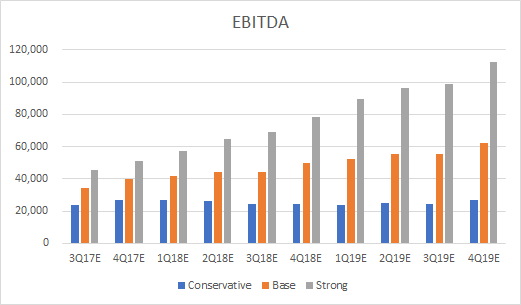
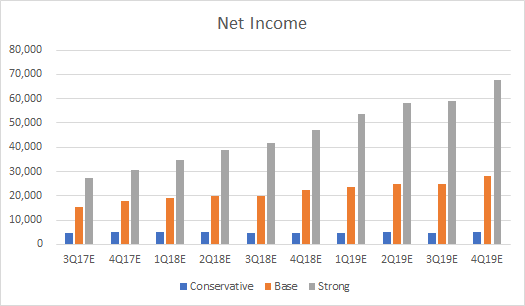
Chart 1, 2, 3: Revenues, EBITDA and Net Income Projections (Source: BSIC)
Share Valuation
The Residual Income Method was used for our valuation of GRUB. This method is ideal for valuing firm’s that do not yet pay dividends or generate positive free cash flow. Note that residual income is the income generated by a firm after accounting for the true cost of its capital. A key metric for the Residual Income Method is equity charge which is the firm’s total equity capital multiplied by the required rate of return of that equity (estimated typically using the capital asset pricing model).
Equity Charge = Equity Capital x Cost of Equity
The required annual return (discount rate) for Grubhub was calculated using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). Assuming a 3-month Treasury rate of 1.06%, an equity market risk premium of 5.05% (KPMG estimate), and a beta of 1.52 (BSIC estimate), the required annual return on Grubhub stock is 8.74%.

Source: CFA Institute
The formula for finding intrinsic value with the Residual Income Model is as follows:
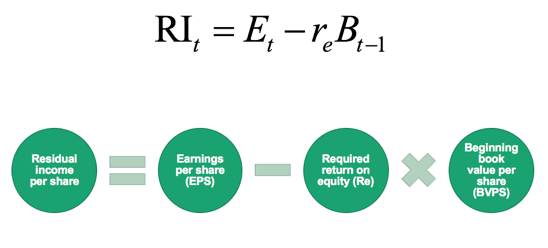
(Source: CFA Institute)
The top formula says, the Value of equity = Book value + PV of residual income during the initial stage + PV of the continuing residual income after the initial stage. For calculating PV of the continuing residual income after the initial 10 quarters of revenue projections, a persistence factor (omega) of 0, 0.62, or 1 is assumed based on whether growth of residual income will fade soon after, taper off based on historical averages, or persist indefinitely.
Residual income is in the numerator of the residual income valuation formula and can also be solved on a per share basis. Residual income per share equals earnings per share minus required return on equity as seen in the formula above.
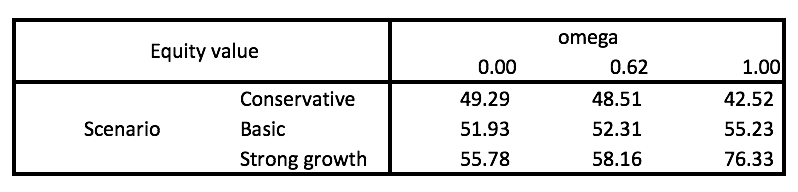
These are the intrinsic share price projections based on our three revenue growth scenarios and omega values regarding residual income projections following FY19.
Intrinsic Share Price (Friday, 6 October GRUB Closing Price – $51.29)
Upside (Downside)
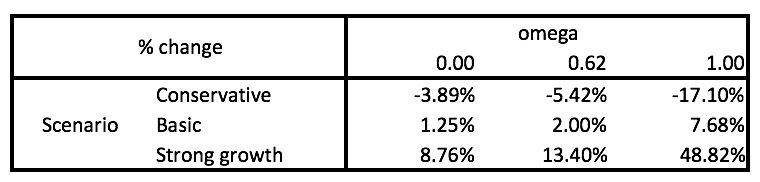
In the base case scenario with omega at historical averages, it appears future growth prospects are priced in accordingly and GRUB is trading just marginally below its $52.31 fair value estimate. However, GRUB is a unique business in a frontier industry, as noted by its intrinsic share price estimations in strong growth scenarios. Future growth projections for GRUB are more likely to settle at either conservative or strong growth scenarios, given that GRUB is jockeying with Amazon and Uber to cement itself as a market leader in this booming new industry. The only concern is that food delivery services for Amazon and Uber can be loss-leading side bets, and they clearly can squeeze out GRUB and remain solvent for much longer if GRUB’s bottom-line growth slows. Chinese ride-sharing service Didi Chuxing did the same thing to Uber in cash burning race to the bottom for the Chinese market, before Uber conceded to a merger to end the price war in August 2016. However, GRUB is sitting on nearly USD $300 million of cash, comprising 23.5% of its total assets. GRUB is the current market leader and has enough ammo to endure a long price war, should the competition for this frontier industry head in that direction.
It is worth noting that 24.91% of GRUB’s float is short, compared with SNAP’s 17.78% and TSLA’s 26.78%. Nevertheless, given the per share intrinsic value, the massive overall industry growth, and the firm’s position as the market leader, we believe GRUB is marginally undervalued yet poised for tremendous growth – our recommendation for the long-term investor is BUY.



0 Comments